Plastic Trays: A Comprehensive Exploration
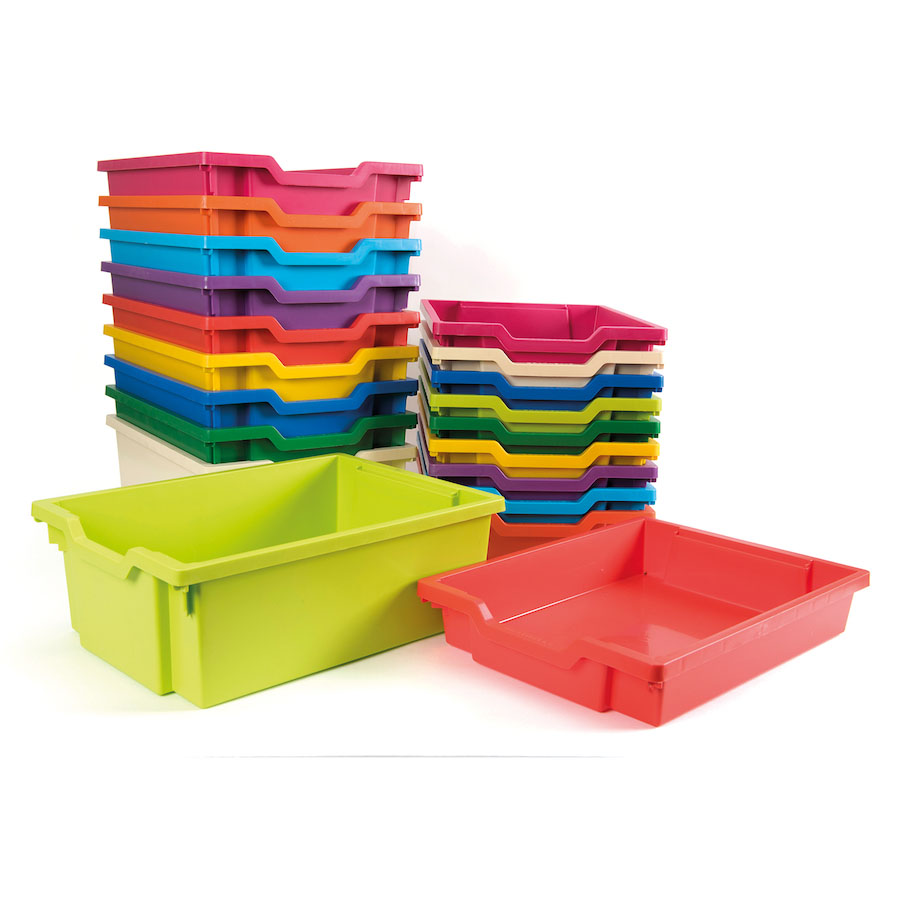

Plastic trays, integral components in the packaging landscape, have revolutionized the way products are stored, transported, and displayed across diverse industries. This comprehensive exploration delves into every facet of plastic trays, from their manufacturing processes to their environmental impact.
Manufacturing and Materials
Manufacturing Process: Plastic trays undergo an intricate manufacturing process involving injection molding or thermoforming. The chosen method depends on factors such as tray complexity, volume, and material type.
Materials Used: The versatility of plastic trays stems from their fabrication using various materials, including PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate), PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), PP (Polypropylene), and HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene). Each material offers distinct characteristics, catering to specific industry requirements.
Applications Across Industries
Food Packaging: In the food industry, plastic trays serve as stalwarts, providing an ideal platform for preserving freshness and ensuring hygiene for perishable items such as fruits, vegetables, meats, and ready-to-eat meals.
Electronics Industry: For the electronics sector, plastic trays become guardians, offering protective encasement for delicate components and devices during transportation. Their inherent shock resistance shields valuable electronic components.
Medical Sector: In the medical field, the role of plastic trays extends to providing sterile and tamper-evident packaging for surgical instruments, medical devices, and pharmaceutical products, adhering to stringent quality standards.
Retail Displays: The transparent and customizable designs of plastic trays enhance product visibility and organization, making them invaluable in retail displays, where efficient shelf presentation is paramount.
Advantages and Characteristics
Durability and Strength: Renowned for their robustness and breakage resistance, plastic trays excel in transporting fragile items, extending the shelf life of perishable goods. Their strength ensures the integrity of products during transit and handling.
Customization and Versatility: The flexible design of plastic trays allows manufacturers to tailor solutions based on specific size, shape, and compartmentalization requirements. This versatility ensures efficient and aesthetically pleasing product presentation.
Cost-Effectiveness: As a cost-effective alternative to materials like metal or glass, plastic trays offer economic benefits, making them suitable for large-scale production without compromising quality.
Sustainability Initiatives: Acknowledging concerns about plastic waste, the industry is actively pursuing sustainable initiatives. Some plastic trays embrace recyclable materials, and ongoing research explores eco-friendly alternatives such as biodegradable plastics and trays made from recycled materials.
Environmental Considerations and Future Trends
Sustainability in Focus: Recognizing the environmental impact of plastic waste, the industry is actively adopting sustainable practices. Manufacturers are exploring alternative materials and designing trays with end-of-life considerations, aligning with global sustainability efforts.
Circular Economy Integration: Plastic trays are increasingly becoming part of the circular economy, with efforts to enhance recyclability, promote reuse, and minimize environmental impact. Industry leaders are investing in closed-loop systems, ensuring the responsible management of plastic tray life cycles.
This exploration of plastic trays traverses their manufacturing intricacies, material versatility, diverse applications, inherent advantages, and the industry’s commitment to sustainability. As plastic tray technology evolves, the delicate balance between functionality, customization, and environmental consciousness continues to shape the future of packaging solutions.